I am so overwhelmed by the response for the WD blog; it encourages me to come up with more topics. Thanks one and all for your comments and email communications.
A couple of days’ back, I was chatting with my friend as he wanted to shift to a new challenging role. After working for several years on SAP platform for one of the Big five companies, he was not satisfied with the kind of work he was doing. I suggested him to go for BIG DATA. He was perplexed by my suggestion and wanted to take some time to think about it. I was taken back this time as he asked me to tell in detail about the BIG DATA. He couldn’t get the information from his peers as well as from his seniors who are having decades of technical and management experience.
I was so pumped to tell him; I love sharing knowledge THAT I KNOW. He was happy to hear me as usual, then I thought why not I write about 'Big data' to encourage my friends who are looking for a career change and for the ones who want to adopt the latest technology that is in demand.
I hope it will help the young talent to understand the difference between Analytics and Big Data so that they can be on the right career track. HERE YOU GO…
In Workday, BIG DATA ANALYTICS plays a major role for the companies to streamline their data.
I have come across a nice quote to start with -----------------------------------------------“In God we trust, all others must bring data” – W. Edwards Demming, Manufacturing Guru and Statistician
Analytics, to put simply, is helping businesses with data. Data can be any information about the system or surroundings.
If a person doesn’t feel well, he/ she might experience a fever or any other anomaly in the body, which indicates that there’s something wrong. Similarly...this data about the system or surroundings of a business is shouting if something is wrong. Analytics is all about identifying and capturing this shot and transforming it into a corrective action.
Let’s take an example, how can analytics help in running a factory? The main components of a factory are machinery, human capital and real estate infrastructure. It will be a great relief to the management instead of routine checks if we can predict when a machinery will develop a slag or when can we expect the workers to go on strike or leave their jobs. It’s too hard to imagine to be worked out, but there is a solution for this …
Yes, analytics can help in doing all this. Machines are made up of a number of components. When a machine is not working properly, some components may have been damaged. If we can place sensors in appropriate regions of a machine and track their output, using historical data, we can very well predict when a damage is about to happen to the machine in real time based on a live feed from these sensors. A recent study by one of the top consulting firms elaborates on how advanced analytics can improve manufacturing to reduce process flaws, save time and money. And the applicability of analytics is practically limitless. From helping run businesses better to saving lives in the field of healthcare, analytics are everywhere. If it’s not anywhere, it will be in the next few years as more and more firms and industries are understanding the importance of analytics and implementing the same.
Analytics has always been around us. We make a lot of day-to-day decisions based on data floating around us and now this is growing as a professional field of study. Analytics will definitely stay and grow!
BIG DATA ANALYTICS
Definition: According to the information technology research and advisory firm Gartner –“Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing for enhanced insight and decision making.”
Big Data in today’s world
Software and Information Technology has made it possible to generate extremely large amount of data which is generated in real time, typically these data sets are of sizes which cannot be processed using traditional database management systems or other data processing software. In the language of big data sizes, we do not deal with gigabytes rather the data size ranges from hundreds of petabytes to Exabytes (1 million terabytes) of data. Now the biggest questions are –how can an organization make effective use of this data to predict upcoming scenarios and trends and how can it use this raw data to optimize its processes in order to increase efficiency, reduce costs and approach unexplored avenues?
Mining Terabytes or Petabytes of raw, unprocessed data is a very complex task and then drawing out meaningful, relevant insights is an even more complex task, the skills needed to mine this data is what matters in today’s fast changing world.
Big Data technologies:
Hadoop an open source framework from Apache is the leading one used globally. This framework, which is a set of tools allows processing of large sets of data by breaking into clusters. Unlike in traditional computing the processing capability using Hadoop can be scaled up from single servers to thousands of machines. The two main components of Hadoop Distributed file System (HDFS) and Hadoop MapReduce. HDFS is a distributed file system designed to run on a fault tolerant, low cost hardware known as commodity hardware. MapReduce, which is based on the Google’s search technology, distributes large data sets across multiple servers which individually do their processing of partly allocated data sets. LinkedIn is one of the companies that use Hadoop to give real time personalized recommendations.
Analysts believe that 90% of the total data is created in the last few years and this pace is accelerating. It will not be a surprise when companies start to deal with Yotta bytes of data in the coming years. Businesses already have realized the importance of Big Data and started investing substantial amount of their capital into it. Big Data is the future, it has been a trending technology recently and soon we may see many advocates for it in the coming years.
Major components of Big Data
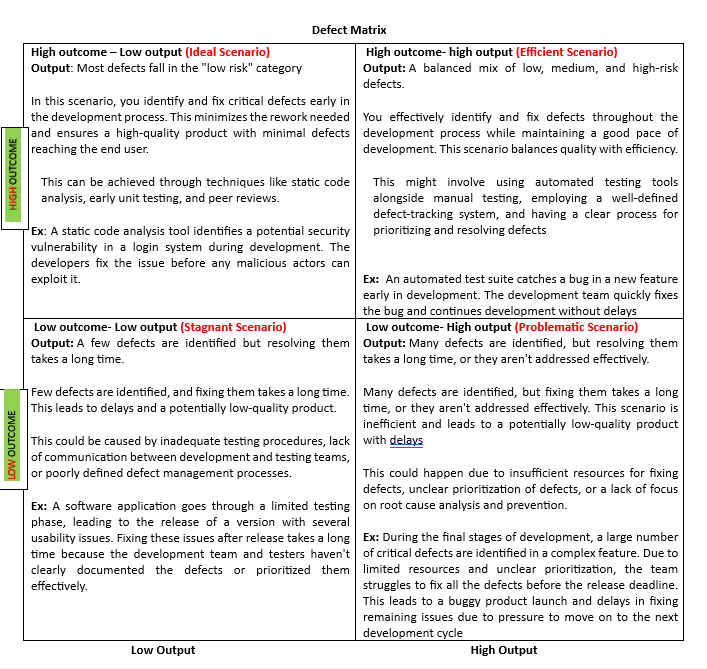
According to industry experts Big data can be categorized into four main components when applying Big Data in real life business operations –, known as the “Four V’s”:
The 4 V’s of Big Data
Volume
When we talk of big data it is implied that we are dealing with enormous volumes of data, this data is typically generated by business processes, automated machines and social networks so the volume of data to be analyzed is massive in size. If we take social networking sites as an example where posts, twitter messages, photos, video clips, etc. Are being generated and shared every second, then we deal with data of the order of Zettabytes or Exabytes. In a research it has been found that all the data generated in the world between the beginning of time and 2014 is equal to the data, which is being generated in a single day after 2015
Thus, data sets are becoming more and more complex and too large to store therefore analyzing data using traditional database technology is often not possible.
Variety
Variety in Big Data jargon refers to the multiple different sources from where data is generated and types of data which can be structured or unstructured. Earlier the majority of data was structured data that stored in relational databases, e.g. Financial data, sales data.
But as technologies have evolved in recent years at a breakthrough pace, almost 80% of data is unstructured in the form of emails, photos, audios, videos, PDFs and social media updates.
With proper implementation of big data technology,we can now make efficient utilization of unstructured data and bring it together with structured data.
Velocity
Advanced technologies have increased the rate at which new data are generated, this data is not localized to any particular region rather it moves around the whole world at a tremendous speed, this flow of data is massive in volumes and continuous.
E.g. Social media post or videos on YouTube, which goes viral in seconds.
Big Data offers the capability to analyze this real time data and allows businesses and industries to make strategic decisions in real time.
Veracity
The data being generated is often raw and unstructured so Veracity refers to the trustworthiness of data, the information which is gathered from various networking sites, business processes or automated machines differs vastly in each instance it becomes difficult to control the quality and accuracy of data. So it is important to differentiate which data are to be mined to draw meaningful insights for analyzing a problem.
We are drowning in data. The volume of data being generated every second is enormous and the rate is increasing exponentially. We have come a long way into a digitized world where every human action is associated with data generation. Social media websites such as twitter and Facebook daily generate data in zeta bytes. In future, it is widely believed that biggest data is not created by humans,but by the ‘Internet of things’. Internet of things is a scenario in which objects equipped with unique identifiers and they automatically communicate by transferring data without human intervention.
How will different industries use Big Data?
Big Data is expected to bring a lot of benefits to the consumers in the form of improved services, more user-friendly systems and thereby resulting in a more transparent dealing of services.
Big Data can affect all industries starting from Banking, Healthcare, Consumer goods, Information Technology and also the Government services. Gartner predicts that BIG data development will drive up IT spending to $232 billion by the end of 2016. All this is possible only when all organizations and the governments are able to fully start using Big Data and reap its benefits.
With the rise in social networking websites, consumers have found a platform to connect with each other and this helps the organizations capture a lot of data with the help of data analysts. In a nutshell, there is data everywhere and hence it becomes highly important to make use of it for the benefit of the organization and the overall economy.
Big Data in Marketing
Big data is going to shape the products in the new age market. With the customer insight gathered and consumer behavior studied,it is much easier for marketers come up with customized products. The companies who are succeeding are not the ones having the most data, but the ones who are using the data the most.
In the future product development would be hugely backed by Big Data results and it would be surprising if this becomes an important competitive strategy for companies.
Big data in Retail
In the near future, for the conventional Brick and Mortar shops, big data can be a reviving force through video surveillance and conversational analysis
Big data is all poised to be detrimental factor in Airport, Rail, Energy and Social Services through its services.
In a nutshell, we are moving to a concept of SMART CITY and Big data with its other technologies like Cloud Computing, Multi Sensors and Intelligent are going to herald the Smart City Concept.
Big Data in Agriculture
John Deere the US agricultural, equipment manufacturing company has led the way in heralding the big data advent in agriculture.
Big data are used by farmers to figure out the choices of the crop, when and where to plough, and where will the best return come from. Sensors in Tractors, Historical data on soil conditions, weather prediction and crop features.
Big Data is promising a future in Agriculture wherein lands would be highly productive and farmers well profited. Big data strives for a self-sufficient mode.
Recording of data takes place at the most of the simplest of the tasks like the purchase of groceries to the most complex form of utility( e.g. Smart phones).
This count is growing each day and every second and hence categorized as Big Data. Currently these large units of data inventory are growing beyond the ability to be managed and analyzed with traditional data processing tools. The initial idea was to control the size of this information to free up the memory of the computers for a new set of growing data. This led to the introduction of new technologies like Google’s MapReduce and open-source Yahoo’s Hadoop and more. Data collected is used by many internet companies to gain significant competitive advantage in the market. As time passes by, companies have to change their business models to survive and hence this massive change can be categorized as data-driven technological revolution of which we are all a part of.
WORKDAY BIG DATA ANALYTICS:
It is very helpful to make smart decisions for manager, employees and executives with the valuable information that they get.
With workday BIG DATA ANALYTICS we can integrate, analyze and visualize data from workday and non-workday data to identify the root causes, detect patterns and trends and predict accurately and all this can be done by a single application.
WORKDAY BIG DATA ANALYTICS enables organizations’ to answer business questions such as, how we are measuring performance accurately.
Ex: We can augment workday performance data with sales data from CRM systems to determine the average sales performance rating.
To get a clear picture whether worker performance matches the rating, we can drill down to get a closer look at the matrix within the performance rating. This gives the information you need to know to make smart investments in your talent. By using existing capabilities within workday,such as custom fields. We can view worker data coming from data sources outside of workday to give an inside view of low-level details used in reports. Workday BIG DATA ANALYTICS makes it simple to match together from workday and non-workday data source with built in data connectors to common gate resources. Data analysts can easily connect to any data source of any type at any volume with easy to use interface on data analysts with tools to quickly and easily exploring combined data from multiple sources with hundreds of built in functions. Data analysts can perform simple joins and filters with more advance analysis, such as ‘ Forecasting’.
BIG DATA has built in pre-defined templates such as market compensation analysis, retention risk and impact analysis, Global payroll cost analysis and more. Workday BIG DATA analytics are unified with the rest of the workday. It requires no separate infrastructure and no separate security. The best part is reports generated by workday BIG DATA ANALYTICS are treated the same with any other reports/reporting in the workday so that we can quickly gain insight and take necessary actions.